Introduction
Proper nutrition during childhood is critical for growth, development, and overall well-being. However, many children are at risk for nutritional deficiencies that can affect their health. This guide provides an overview of the most common vitamin deficiencies and mineral deficiencies in children—iron, vitamin D, and calcium—and offers practical tips to prevent them through a balanced diet.
COMMON NUTRITIONAL DEFICIENCIES IN CHILDHOOD
Children undergo several development changes up to 5 years of age. It is a critical period of child growth. Micronutrients have an important role in promoting growth and development of children. Minerals and vitamins help in the production and function of enzymes, hormones and growth regulator proteins. They also help in maintaining appropriate oxygen levels in the blood.
Nutritional deficiency under five years hampers a child’s growth, leading to underweight, stunting, cognitive impairment and behavioral, disorders. It also makes children susceptible to chronic health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, osteoporosis, rickets, anemia, cancer, stroke, and heart disease at an early age.
The Most common micronutrient deficiencies among School children are caused by calcium, folate, iron, magnesium, potassium, and vitamins- A, D and E. Studies have shown that approximately 5 lakh children are becoming blind due to vitamin A deficiency and at the same time 41.7% of children worldwide are at risk of anemia due to iron deficiency.
Social problems caused by kids’ vitamin deficiencies in addition to health issues are less schooling, decreased academic performance and reduced economic productivity. This blog will provide some of the key SIGNS OF VITAMIN AND MINERAL DEFICIENCIES IN CHILDREN.
Iron Deficiency

Iron is an essential mineral that binds to hemoglobin in blood to carry oxygen throughout the body.
Iron deficiency in children leads to anemia, a condition in which blood does not have enough RBCs. Children who consume an iron-deficient diet are at high risk of iron deficiency. Symptoms of iron deficiency:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale skin, lips, and nail beds
- decreased appetite
- Delayed brain development
- Behavioral problems, such as irritability, difficulty concentrating, and reduced attention
Vitamin D Deficiency
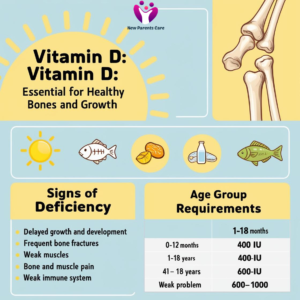
Vitamin D is a crucial nutrient for the development of the skeletal, brain, and immune systems. It is vital for the body’s absorption of calcium and phosphorus. The requirements of vitamin D according to the age group are given below
| Age group | Requirement |
| 0-12 months
1-18 years |
400 IU
600-1000 IU |
Mineralization of bones depends on the availability of vitamin D. Children with darker skin tones, higher body fat, or limited sun exposure are more prone to vitamin D deficiency, which can result in rickets—a condition that causes bones to weaken and become brittle. Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency:
- delayed growth and development
- bone fractures
- weak muscles and difficulty in coordination
- frequent bone and muscle pain
- dental problems
- weaken the immune system
Zinc Deficiency
Zinc has a crucial role in the synthesis of DNA. It aids in improving the immune system, brain functioning, and wound healing. Health problems due to Zinc deficiency are retarded growth, weak immunity, and increased exposure to infections. Premature infants who are not breastfed are at higher risk of zinc deficiency.
Symptoms of Zinc deficiency in children include:
- stunted growth
- sexual maturation
- Diarrhea
- delayed wound healing
- skin rashes and lesions.
- lack of appetite
- hair loss
Calcium Deficiency

Calcium is an essential mineral for children’s growth and development of strong bones, muscles, and teeth.
Low levels of calcium lead to hypocalcemia. Children who consume a diet deficient in calcium are at high risk of developing hypocalcemia. Calcium deficiency symptoms:
- weakened bones
- fractures
- Neuromuscular impairment
- Cognitive impairment
- Reduced concentration
- tooth decay and other dental problems.
- Tiredness and weakness
HOW TO PREVENT NUTRITIONAL DEFICIENCIES IN KIDS
Nutrient deficiency diseases in children can be prevented and treated with supplementation of a balanced nutritious diet and incorporating healthy eating habits. Some preventive measures that support your child’s growth are given below
1) Ensure that your child has a balanced and varied diet
To prevent nutritional deficiencies in children, it’s important to ensure they have a well-balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
2) Encourage healthy snacking in your child
Choosing fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole-grain snacks with balanced calories is a healthier alternative to processed, high-calorie options.
3) Encourage your child to drink more water
Water is an important component to make the children stay hydrated and promote overall health. It also helps prevent constipation. Suggest your child to drink more water throughout the day.
4) Exposure to sunlight
Vitamin D is produced by the sun which aids in strengthening bones. Exposure to sunlight before 10 AM is best due to low UV index Sunlight exposure before 10 am is best due to the low UV index.
5) Supplement your child when necessary
Supplements such as multivitamins and minerals can help meet the children’s nutrition demands who are unable to absorb nutrients from the normal diet. It’s essential to consult a pediatrician for the dosage of supplements.
6) Encourage physical activity in your children
Motivate your child to engage in at least one hour of physical activity daily, as it helps strengthen muscles and bones while also enhancing concentration.
7) Discourage processed foods
Processed and junk foods are high in refined carbohydrates, salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats. Limiting these foods can help maintain a healthy weight with additional health benefits.
8) Encourage breastfeeding in infants
Breastfeeding helps prevent nutritional deficiencies in infants, as mother’s milk provides a well-balanced mix of nutrients that are easily digestible and support long-term nutritional health.
In the event your child shows signs of nutritional deficiency, it is essential to talk to a pediatrician for proper evaluation and treatment. He will recommend dietary, lifestyle, and supplements to fulfill the children’s nutrition requirements of your child.
Conclusion
Nutritional deficiencies can have long-term effects on a child’s development, but they can be prevented through mindful dietary choices. By ensuring that children get a balance of essential nutrients like iron, vitamin D, and calcium, parents can support their children’s growth and overall health.
Join Our Parenting Community:

Need personalized recommendations for your child? Join our exclusive WhatsApp Group where you can get advice on topics like picky eating, sleep routines, and more, directly from experts and fellow parents! You’ll also be the first to know about new tips, tools, and articles.
Explore Our Handy Tools:
We’ve got a bunch of free tools to make parenting easier! Check them out:
- Baby Name Generator: Find the perfect name for your little one.
- Ovulation Calculator: Track your fertility and plan your pregnancy.
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator: Monitor your pregnancy progress with ease.
- Chinese Gender Predictor: Curious about your baby’s gender? Have fun predicting!
Stay Connected with Us:
For more tips, parenting hacks, and fun ideas, follow us on:
Join the conversation and get daily inspiration for your parenting journey!
Stay connected and let us help you on your parenting journey!
